computer science
Flyweight 패턴
sundotcom
2025. 4. 20. 18:50
Flyweight Pattern
fit more objects into the available amount of RAM by sharing common parts of state between multiple objects instead of keeping all of the data in each object
refactoring.guru
head first design patterns 서적

- 인스턴스가 매우 많이 생성될 때, 인스턴스 생성 비용이 높은(하지만 모든 인스턴스가 공유하는 uniqueState) 필드가 있다면, 해당 필드는 공유하고 반복되는 state는 cache를 하면 메모리 절약 가능
- 위 예시에서는 20KB를 차지하는 sprite는 공유하고, 반복적으로 생성되어 각 인스턴스에 할당되어야 하는 필드들은 새로 할당
- 이 때, particle, coords, vector, speed를 가진 MovingParticle 인스턴스는 immutable 해야 함
- 동일한 플라이웨이트 객체가 다른 context에서 사용될 수 있으므로 해당 상태를 수정 불가능으로 만들어야 함. 플라이웨이트는 생성자 매개변수를 통해 상태를 한 번만 초기화해야 함. setter나 public field를 다른 객체에 노출해선 안됨
- Since the same flyweight object can be used in different contexts, you have to make sure that its state can’t be modified. A flyweight should initialize its state just once, via constructor parameters. It shouldn’t expose any setters or public fields to other objects.
- Flyweight Pattern은 단지 최적화를 위해서 사용해야 함
- 적용하기 전에 프로그램이 메모리에 유사한 객체를 대량으로 가지고 있어 RAM 소비에 문제가 있는지 확인하여 필요에 따라 적용해야 함
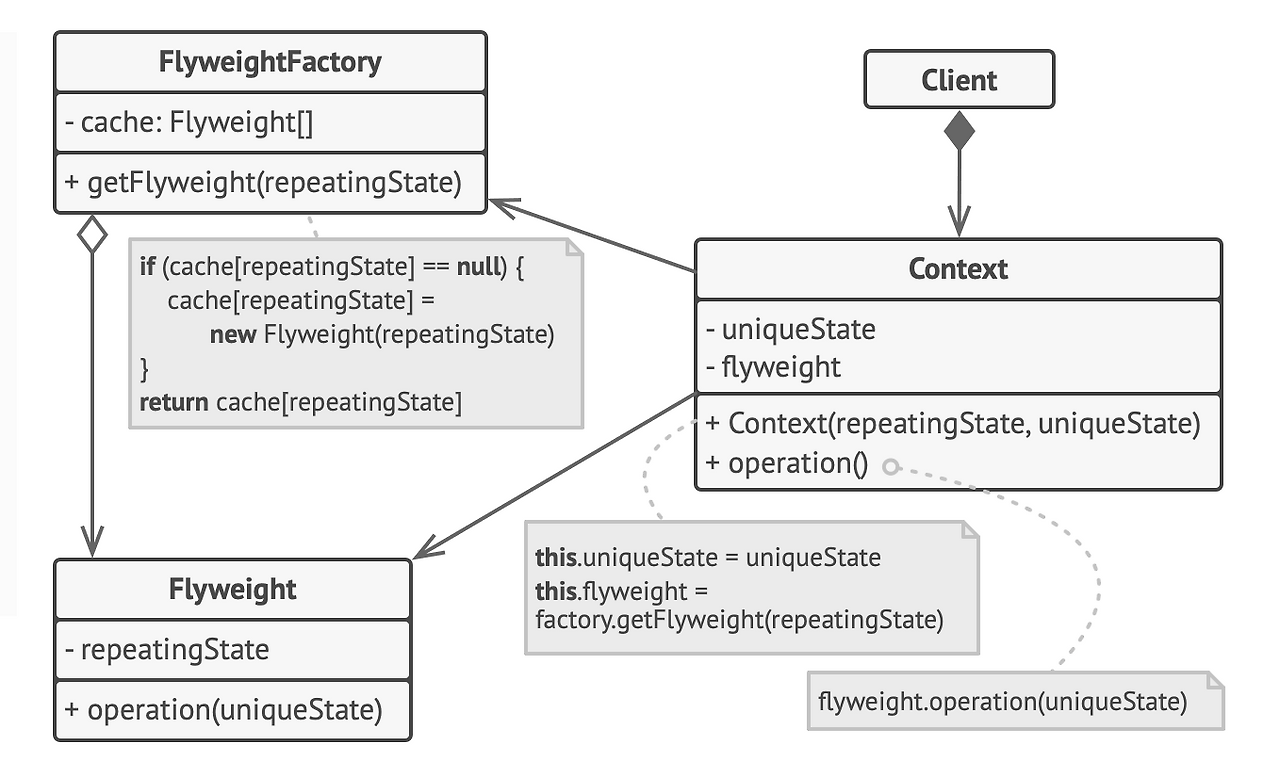
- Flyweight
- 여러 인스턴스가 공유하는 Context의 field(uniqueState)를 포함하여 사용 가능
- 반복적으로 사용되어지는 repeatingState는 flyweight 인스턴스 생성 시 최초에만 초기화
- Context
- 실제 모든 fields(uniqueState & flyweight)를 포함하는 original 객체
- Client 코드가 의존하는 객체
- 각 필드들을 초기화하고, 실제 method 행위를 하는 객체
- FlyweightFactory
- flyweight 인스턴스를 cache 하고, 실제 해당 캐시에 접근하는 메서드를 가짐
- 클라이언트가 direct로 Context에서 해당 객체를 접근하는 것이 아니라, Context에서 flyweightFactory의 메서드를 호출해 cache에 접근하여 캡슐화
public class Context {
Object uniqueState;
Flyweight flyweight;
public Context(Object uniqueState, Flyweight flyweight) {
this.uniqueState = uniqueState;
this.flyweight = flyweight;
}
public void operation() {
flyweight.operation(uniqueState);
}
}
public class FlyweightFactory {
Map<Object, Flyweight> cache = new HashMap<>();
public Map<Object, Flyweight> getFlyweight(Object repeatingState) {
if (cache.get(repeatingState) == null) {
cache.put(repeatingState, new Flyweight(repeatingState));
}
return cache;
}
}
public class Flyweight {
Object repeatingState;
public Flyweight(Object repeatingState) {
}
public void operation(Object uniqueState) {
// do sth..
}
}
- Pros
- RAM 용량을 획기적으로 절약 가능
- Cons
- 누군가 flyweight 메서드를 호출할 때마다 context data 중 일부를 다시 계산해야 하는 경우 코스트 증가
- 코드 복잡도가 높아짐